Are you ready to embark on a journey into the world of civil engineering? The Junior Instructor – Draughtsman Civil exam, conducted by the Industrial Training Department, is your gateway to a rewarding career in this dynamic field. Let’s dive into the details:
Junior Instructor Draughtsman Civil Exam Overview
- Post: Junior Instructor – Draughtsman Civil
- Category: Direct Recruitment (CAT.NO. 657/2023)
- Vacancy: Anticipated
- Exam Date: September 11, 2024 (Wednesday)
- Confirmation Date: June 23, 2024, to July 12, 2024
- Mode of Examination: Online (OMR)
- Total Marks: 100
- Duration: 1 hour 30 minutes

Junior Instructor Draughtsman Civil Last Recruitment Details
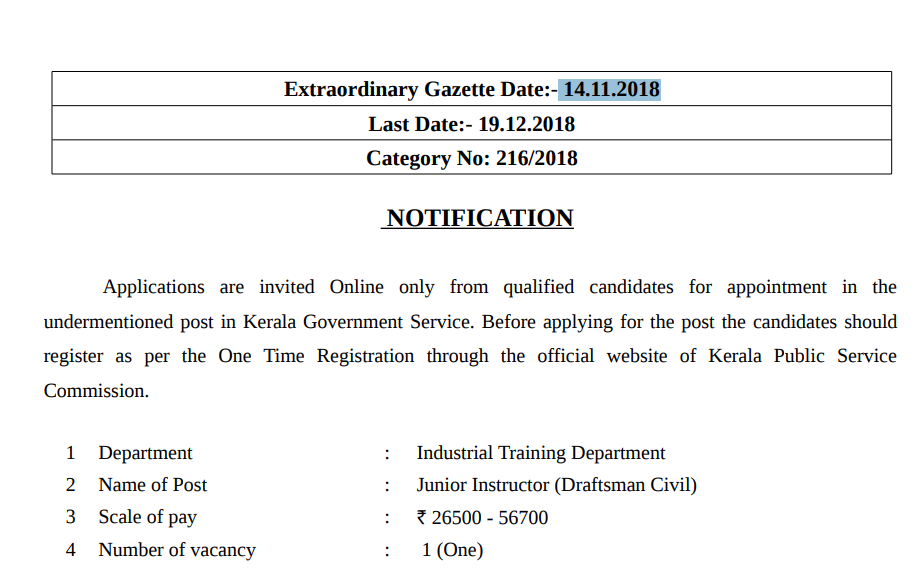
- The notification for the Junior Instructor (Draughtsman Civil) position was issued on November 14, 2018, with one reported vacancy.
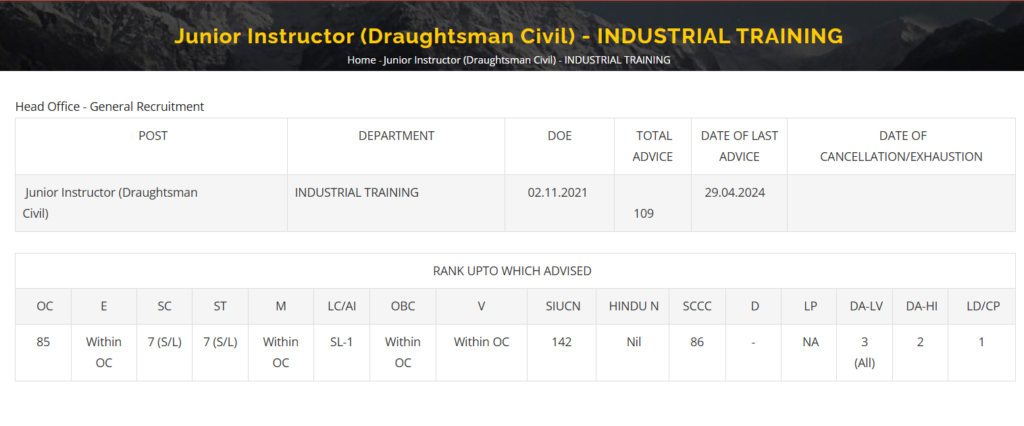
- Following the interview process, a ranked list was established, which came into effect on November 2, 2021. The main list included 169 candidates.
- Subsequently, 61 additional vacancies were reported—49 fresh vacancies and 12 non-joining duty (NJD) vacancies.
- A total of 109 advice memos were sent from the ranked list, with the most recent advice sent on April 29, 2024.
Syllabus of Junior Instructor Draughtsman Civil
Building Materials (15 marks)
- Rock, Stones, Brick, Lime, Cement, Pozzolanic Materials:
- Classification, types, and uses.
- Clay Products:
- Earthenware, stoneware, porcelain, terracotta, and glazing types.
- Mortar:
- Preparation, classification, types, and uses.
- Concrete:
- Preparation, classification, types, and uses.
- Timber:
- Structure, defect classification, seasoning, and uses.
- Admixtures:
- For cement mortar and cement concrete, classification, types, and uses.
- Paints, Varnishes, Metals, Plastics:
- Classification, types, and uses.
Construction Technology (15 marks)
- Components of a Building:
- Understanding the various elements.
- Stone Masonry and Brick Masonry:
- Types and classification.
- Composite Masonry:
- Elements and types of bonds.
- Arches:
- Technical terms, types, centering, and lintel types (wooden, brick, stone, steel, RCC).
- Foundations:
- Construction details of shallow and deep foundations.
- Types of foundations: well foundation, special foundations, pile foundations, and foundations on black cotton soils.
- Permanent and Temporary Structures:
- Life of structures, substructure, superstructure, load-bearing structure, cavity wall, framed structure.
- Formwork, scaffolding, shoring, underpinning, and partition requirements.
- Treatments for Building Structures:
- Damp proofing courses, anti-termite treatment, weathering course materials, properties, functions, types, objectives, and methods.
- Fireproofing and its effects.
- Carpentry Joints:
- Terms, classification of joints, and uses/types of fixtures and fastenings.
- Doors, Windows, and Ventilators:
- Parts, location, standard sizes, and types.
- Floors:
- Ground floor and upper floor types.
- Flooring materials used and types.
- Roofs and Coverings:
- Purposes, elements, and types (flat, pitched, truss, king post, queen post, Mansard, Bel-fast, steel, composite).
- Shell types (North-light and double-curved).
- Components of a dome.
Building Drawing and Planning (10 marks)
- Layout of Drawing:
- Understanding the arrangement of elements in architectural drawings.
- Lines, Lettering, Dimensioning, Scales, and Projection:
- Techniques for creating clear and accurate drawings.
- Importance of B.I.S. (Bureau of Indian Standards):
- Introduction to the Code of Practice for Architectural and Building Drawings (IS: 962-1989).
- Principle of Planning:
- Objectives, importance, functions, and responsibilities.
- Orientation considerations.
- Local Building Bye-Laws:
- Adherence to regulations as per ISI Code.
- Layout Plan and Key Plan:
- Understanding and creating layout plans.
- Submission Drawing:
- Preparing drawings for submission.
- Provision for Safety:
- Incorporating safety measures in building design.
- Requirement of Green Belt and Land:
- Understanding environmental considerations
R.C.C. and Steel Structures (10 marks)
- Reinforced Concrete (R.C.C.):
- Materials, proportions, and characteristics.
- Method of mixing concrete and slump test.
- Formwork and steel behavior.
- Bar bending details as per I.S. Code.
- RCC Structure:
- Columns, beams, and slabs (one-way and two-way).
- Innovative construction techniques.
- Retaining walls and safety against earthquakes.
- Steel Structures:
- Common forms of steel sections.
- Structural fasteners and joints.
- Tension and compression members.
- Classification and fabrication.
- Construction details.
Public Health and Sanitary Engineering (5 marks)
- Terms Used in PHE:
- Understanding terminology related to public health engineering.
- Systems of Sanitation:
- Different approaches to sanitation.
- House Drainage and Plumbing Systems:
- Design and implementation.
- Sanitary fittings.
- Purification of Water:
- Methods and processes.
- Types of Sewer Appurtenance:
- Manholes and septic tanks.
- New plumbing technologies.
Roads, Railways, Bridges, and Tunnels (10 marks)
- General Principles of Alignment:
- Aligning roads, railways, and bridges.
- Road Construction:
- Classification of different types of roads.
- Components and road curves.
- Road drainage systems.
- Bridges and Tunnels:
- Components of bridges.
- Types of superstructures and substructures.
- Classification of bridges based on IRC loading.
- Selection and alignment of bridges.
- Caissons and cofferdams.
- Classification of culverts.
- Tunnel sizing rules.
- Railways:
- Permanent way components.
- Rail gauges, sections, and length.
- Welding, wear, coning of wheels, and rail creep.
- Fixtures, fastenings, and railway station design.
Irrigation Engineering (10 marks)
- Hydrology:
- Duty, delta, base period, and intensity of irrigation.
- Hydrograph: peak flow, runoff, catchment area, and CCA.
- Understanding Rabi and Kharif crops.
- Storage/Diversion Headworks:
- Characteristics and types.
- Dams, Barrages, and Weirs:
- Classification and purposes.
- Hydroelectric Projects:
- Component parts and functions.
- Canals:
- Classification and distribution system.
- Canal structures.
- Cross Drainage Works:
- Types, including aqueducts, super passages, siphons, level crossings, inlets, and outlets.
Estimating and Costing (5 marks)
- Common Techniques:
- Units of measurement, necessity, and importance.
- Approximate and Detailed Estimates:
- Taking off quantities and methods.
- Rate Analysis:
- Typical items and their specifications.
- Consideration of labor and materials.
- Schedule of rates.
- Estimating Irregular Boundaries:
- Using trapezoidal and Simpson’s formulae.
Surveying and Leveling (10 marks)
- Surveying:
- Instruments employed and common terms.
- Classification: plain and geodetic.
- Techniques: chaining, plane table survey, and compass survey.
- Understanding bearing, included angle, local attraction, magnetic and true bearing, and declination.
- Leveling:
- Principles of leveling.
- Instruments: dumpy level and auto level.
- Levelling staffs: types, components, and functions.
- Technical terms: level, horizontal surface, datum, benchmark, focusing, and parallax.
- Deduction of reduced levels.
- Types of leveling and contouring.
Engineering Mechanics (10 marks)
- Mechanical Properties of Materials:
- Stress, strain, elasticity, Hook’s law, elastic limit, modulus of elasticity.
- Types of stresses.
- Standard stress-strain curve for mild steel under tension.
- Yield stress, proof stress, ultimate stress, and strain at critical points.
- Percentage elongation.
- Centroid and Moment of Inertia:
- Identifying the centroid of geometrical plane figures.
- Moment of inertia (M.I.) for plane lamina and solid bodies.
- Radius of gyration and parallel/perpendicular axes theorems.
- Polar moment of inertia for solid circular sections.
- Friction:
- Types and laws of friction.
- Limiting equilibrium and limiting friction.
- Coefficient of friction, angle of friction, and angle of repose.
- Relationship between coefficient of friction and angle of friction.
- Resolution of Forces and Equilibrium:
- Orthogonal components of a force.
- Composition of forces: resultant and analytical methods.
- Moment of a force, Varignon’s Theorem, torque.
- Equilibrium and equilibrant.
- Lami’s Theorem.
Conclusion
Remember that while the topics listed above are covered, there may be additional questions related to other areas prescribed for the educational qualification of the post. If you have any further questions or need clarification, feel free to ask!
Remember, the key to cracking any exam is consistency and hard work. So, keep practicing and stay focused. Good luck with your preparation!
